Plans for over 130 new homes to be built and Kent villagers are not happy
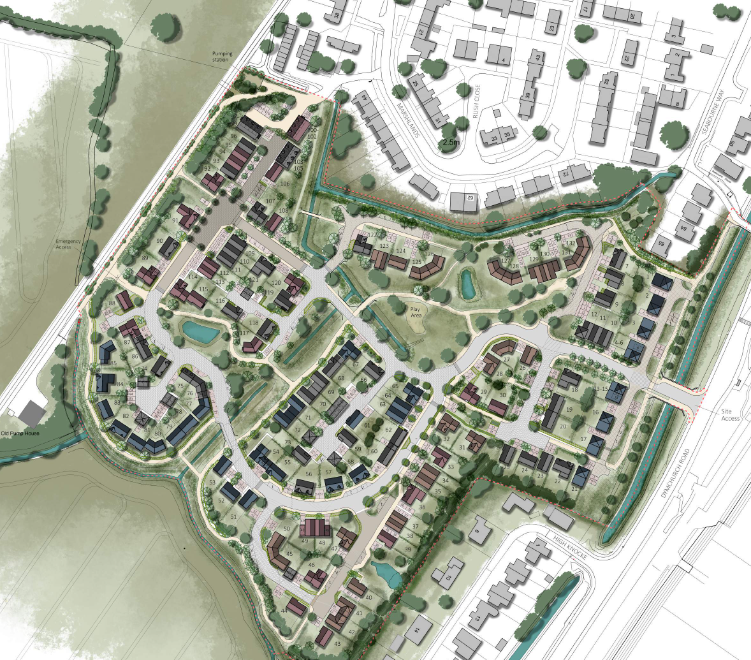
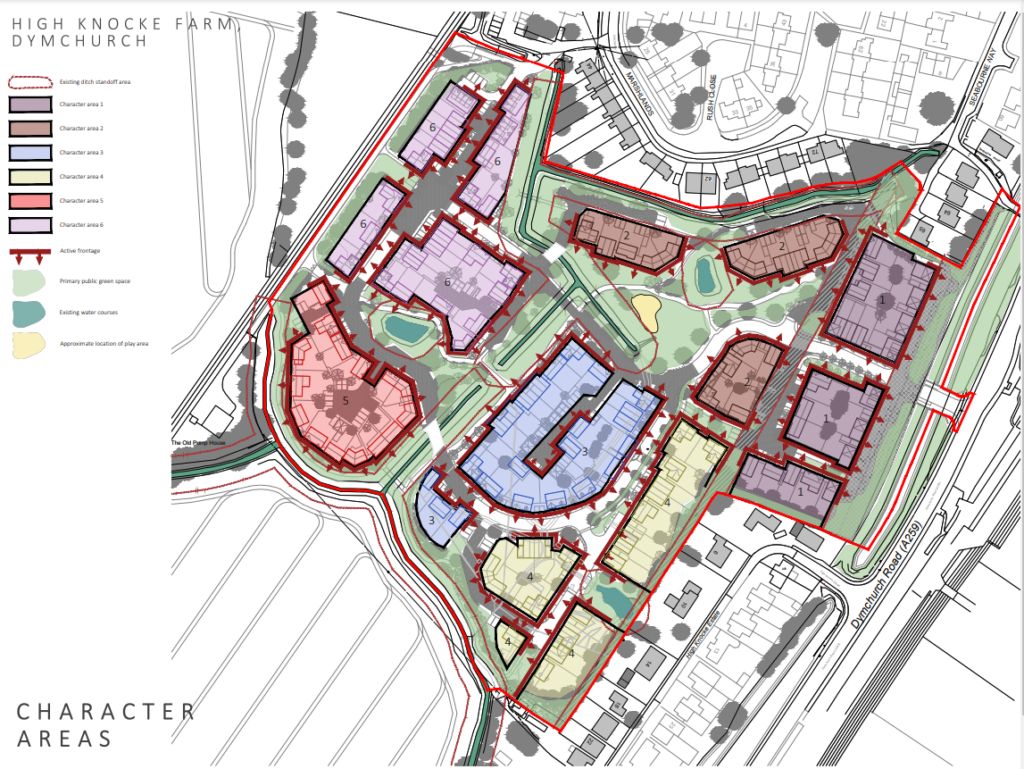
Plans to bring around 132 new houses to the village of Dymchurch have been met with a flood of objections. The planning application for this project has been submitted to Folkestone and Hythe District Council. On the land at High Knocke Farm.
Located roughly about 400 meters away from Dymchurch village centre. The proposed site comprises a total 6.3 hectares of mainly undeveloped greenfield land in agricultural use.
What do the plans propose?
The plans put forward by Redbridge Estates declare that the site offers an opportunity to produce sustainable high quality houses to the Dymchurch area. The houses are proposed to be mainly two storey detached, semi-detached and terrace houses. With a small number of flats alongside them.
In addition, because there is so much land to work with 38% of the site area will be used as public open space. The plans show there are large open community spaces, water course’s, and children’s plan and activity areas.
Although, building a large number of houses might sound like a great idea, many locals disagree. Since the application has been submitted, around 200 comments have been made raising their concerns for the project.
Dymchurch Parish Councillors wrote a group statement that states. “As both current and former Dymchurch Parish Councillors, we jointly feel that is important that we make our voices heard on a proposed development that will have significant impacts on the historic coastal village of Dymchurch. One that potentially will change the face and character of the village forever.
Here are a few comments made by locals on their thoughts and opinions of the plans –
George Baker – As a local resident I highly object to the proposed development. The local infrastructure is already strained at the moment and will not be able to accommodate more residents especially through the tourist months. The proposal of using marshlands as access for the site is ridiculous. The bin men Struggle to fit down this road I can’t see site traffic working.
Kathy Pamphlett – We are sick and tired of all the houses been built already traffic has got a lot worse and how are doctors going to cope we cant get to see them now schools will not have the capacity to cope with more now this planning application should definitely not go ahead leave dymchurch alone it’s lovely as it is.
John william Bloomfield – I object to the proposed plan for 132 houses to be built on the land adjacent to 65 Seabourne Way, Dymchurch. Firstly, because the infrastructure in the village of Dymchurch is insufficient to support the additional residents the scheme would generate. Schools and doctors surgeries are already at full capacity and any further numbers would overload the facilities. The land is currently farm land where sheep graze and the loss of this green field site is not acceptable. Dymchurch is a holiday village and during the summer months the number of residents almost doubles. This scheme would further compound the crowding in and around the village. During construction work additional pressure caused by additional traffic on the A259 would result in further disruption on a very busy road, especially during the summer months.
Find the application here –
Folkestone and Hythe District Council’s planning committee is scheduled to meet and decide on June 6th. Full details on the application and all comments left on the proposals can be found here.