How to make your home more energy efficient?
Before you remodel your home or design a new one you should consider investing in energy efficiency, especially during this cost-of-living crisis. You will save energy and money and your home will be more comfortable.
How energy efficient is your home?
The first step in this process is to find out how much energy your home uses. And what is the most effective way to improve it. If your home has an energy performance certificate, it will help you identify any possible improvements. You can find any current or expired EPC in the UK on the government’s website.
The main aspects of an energy efficient home –
There are often 3 main aspects that are crucial when achieving an energy efficient home design, and they are:
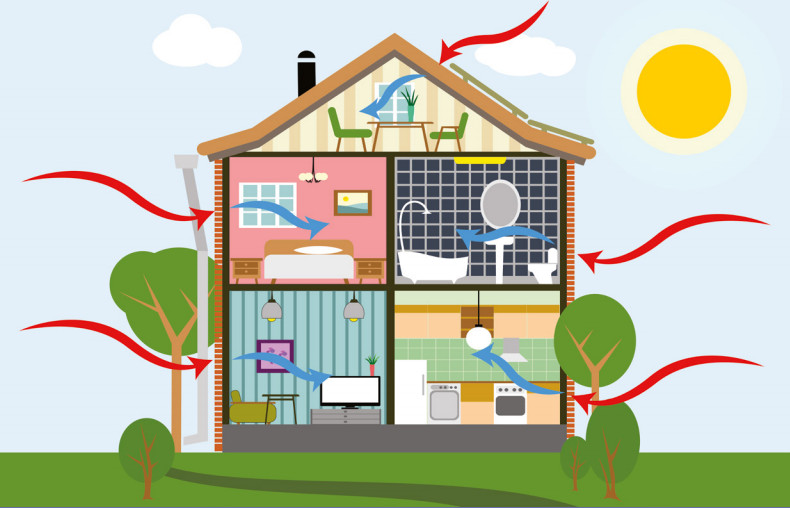
- Air quality –
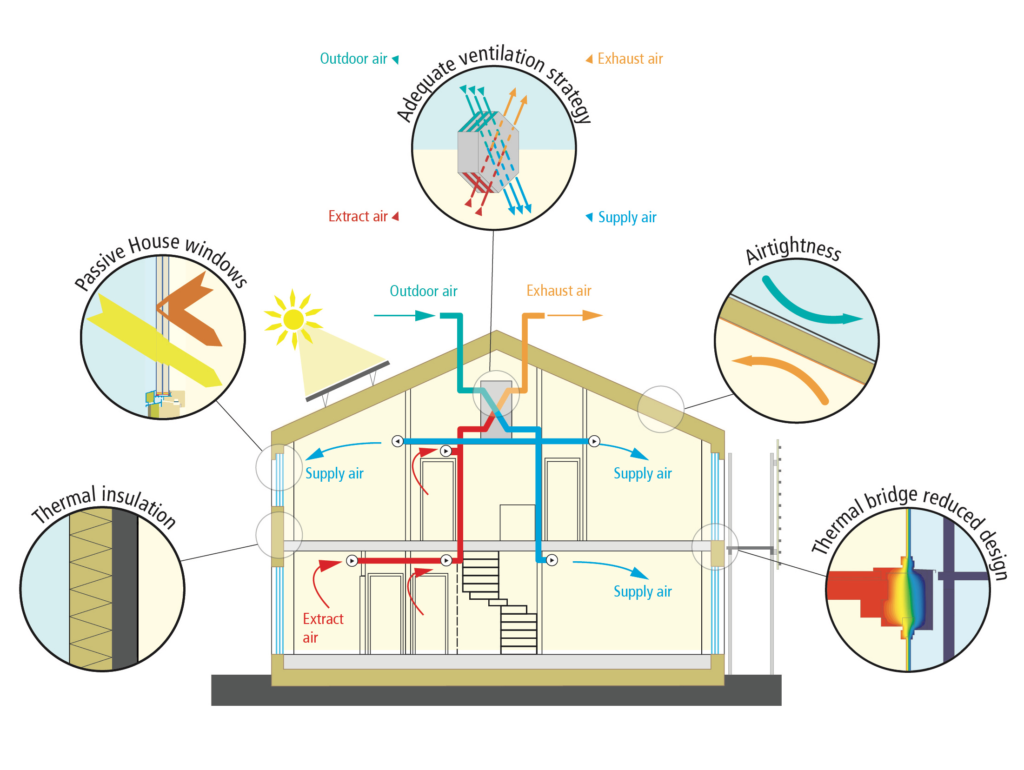
Adding high quality insulation to your home will make it more air tight. The tighter the air the more heat it retains. However, it’s important to install a good ventilation system. This will allow you to remove the moist air that builds up in your home, without losing heat.
- Insulation
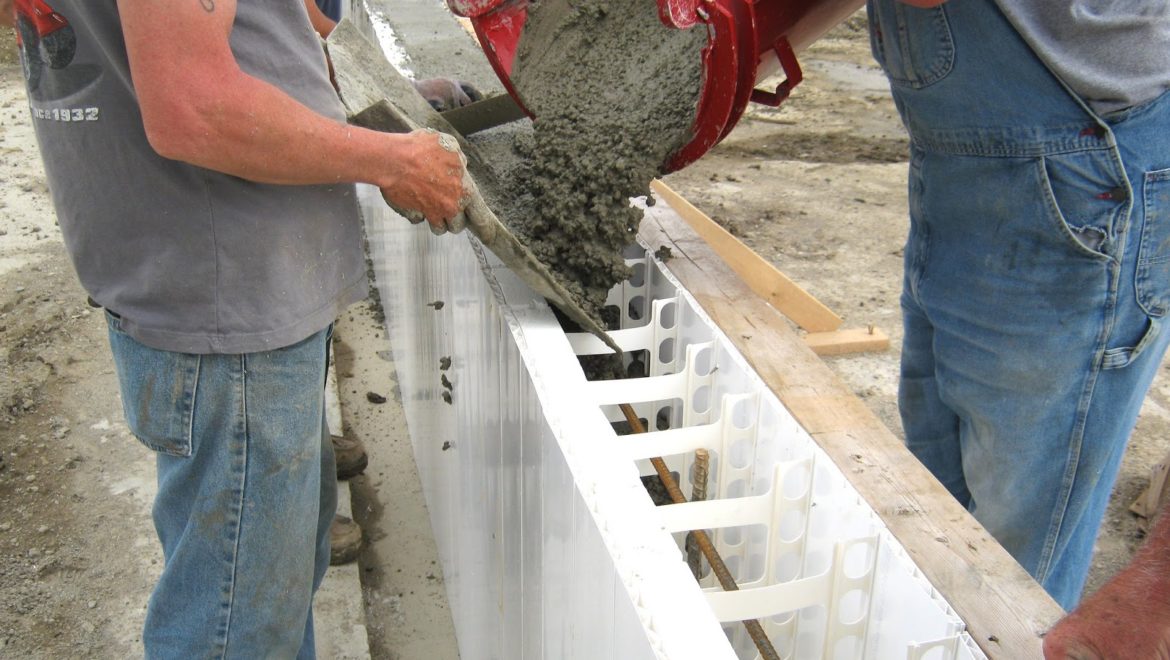
Choosing the right insulation is important when it comes to retaining as much heat as possible. There are many effective ways to insulate your home, which can reduce heat loss. For example: cavity wall insulation, floor insulation, windows and doors, solid wall insulation, etc.
- Heating and cooling –
Since the gas prices are increasing homeowners are looking for the best ways to save some money. Once your home is properly insulated you won’t need as much heat to maintain a comfortable temperature. This is a benefit because you will use less oil, gas or electricity.
Can reducing a home’s energy efficiency help combat climate change?
Homes that use energy supplied from the burning of fossil fuels are responsible for a large amount of carbon dioxide emissions. This means improving the energy efficiency of a home can reduce the burning fossil fuels.