Architectural Influences: A Journey Through the Cultural, Historical, and Global Impact on UK Architecture
Architecture is a dynamic and ever-evolving reflection of a society’s values, beliefs, and history. The United Kingdom, with its rich and diverse cultural heritage, has been significantly influenced by a variety of factors that have shaped its architectural landscape over the centuries. In this blog, we will embark on a journey to explore the cultural, historical, and global influences that have left their mark on UK architecture. From ancient times to the modern era.
Ancient and Medieval Influences
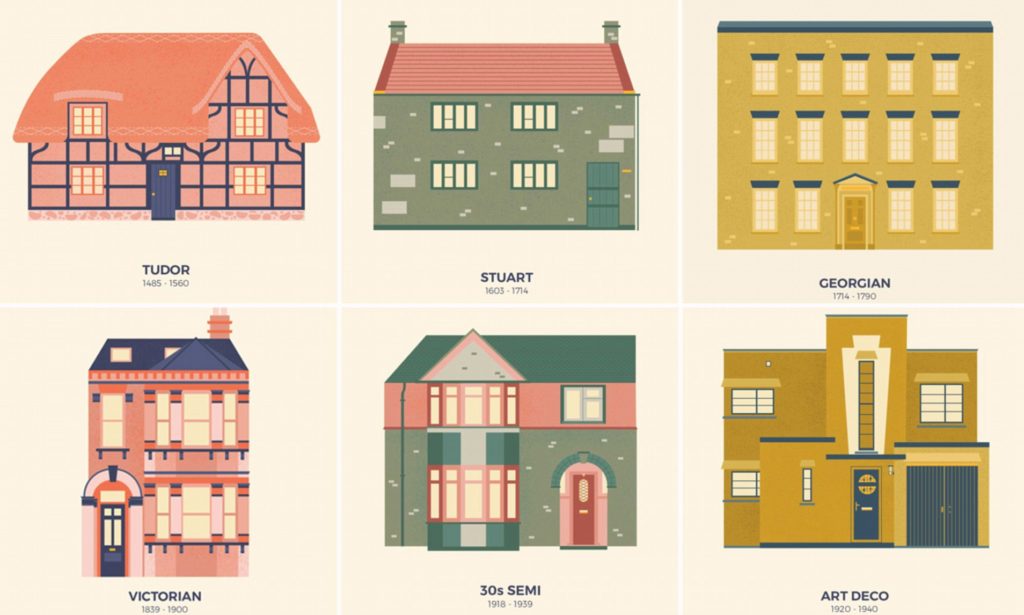
The roots of UK architecture can be traced back to its ancient and medieval past. Celtic, Roman, and Norman influences have all played a role in shaping the architecture of the British Isles. The Romans introduced elements of classical architecture. Such as arches and columns, which can still be seen in buildings like Bath’s Roman Baths and the walls of York.
Gothic Revival
The Gothic Revival movement, which gained momentum in the 18th and 19th centuries, was a response to the Industrial Revolution and a desire to reconnect with the nation’s medieval heritage. Architects like Augustus Pugin and Sir George Gilbert Scott led this movement, and their creations. Including the Palace of Westminster (the Houses of Parliament), exemplify the intricate Gothic style that became synonymous with British architecture during this period.
Victorian and Edwardian Eras
The Victorian and Edwardian eras brought about a significant transformation in the UK’s architectural landscape. The country’s expanding empire and growing economy led to a wide array of architectural styles. Including Italianate, Queen Anne, and the Arts and Crafts movement. Notable examples include the Royal Albert Hall and the terraced houses of London’s Notting Hill.
The Influence of Colonialism
As a colonial power, the British Empire had a profound impact on the architectural styles of its colonies. Particularly in India and parts of Africa. This influence is evident in buildings like the Victoria Memorial in Kolkata, India, with its imposing neo-classical design, and the incorporation of local materials and craftsmanship in colonial-era bungalows.
Modernism and Post-War Architecture
The aftermath of World War II and the post-war reconstruction era saw the emergence of modernist architecture in the UK. Architects like Ernő Goldfinger and Alison and Peter Smithson embraced the principles of functionalism and minimalism, leading to the construction of iconic buildings such as the Royal Festival Hall and the Barbican Centre in London.
Brutalism and Contemporary Trends
The 20th century also witnessed the rise of Brutalism, characterized by the use of raw concrete and bold, sculptural forms. The Barbican Estate and the Trellick Tower in London are prime examples of this style. In recent years, contemporary architecture in the UK has become more diverse, embracing sustainability and drawing inspiration from various global trends.
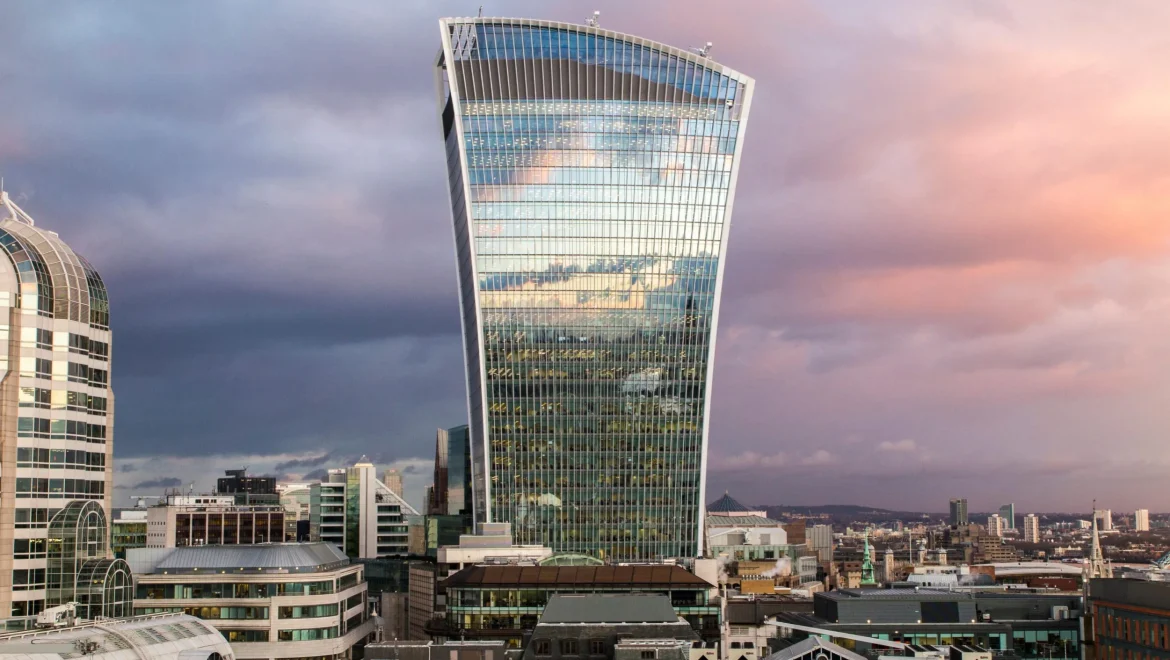
Globalization and the Future
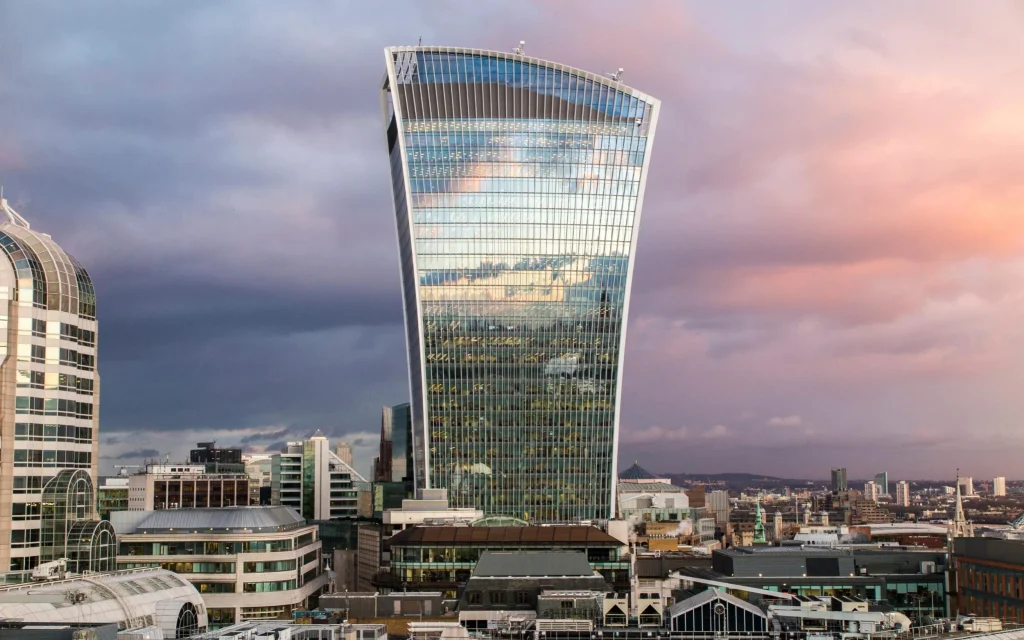
Globalization has had a profound impact on contemporary UK architecture. Architects and designers now draw inspiration from a wide range of international styles and techniques. The Shard, designed by Renzo Piano, is a striking example of this, blending elements of cutting-edge skyscraper design with the global cityscape.
Conclusion
The architectural landscape of the United Kingdom is a tapestry woven with cultural, historical, and global influences. From the Roman arches of Bath to the modern skyscrapers of London, the architectural journey in the UK has been a dynamic evolution. Shaped by the forces of time, culture, and innovation. As the world continues to change, so too will UK architecture. Embracing new ideas, materials, and technologies while maintaining a strong connection to its rich and diverse heritage. The story of UK architecture is a testament to the power of human creativity and adaptability. And it continues to captivate and inspire people around the globe.